Multiple ovarian cysts, PCOS, often accompany obesity, a lot of acne, high testosterone, and irregular menstruation.

Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is characterized by common symptoms such as hirsutism, hair loss, acne, oily skin, and obesity or abnormal weight gain. This condition can occur if you have 'androgen syndrome' or 'too much testosterone'. If you want to learn more, you can understand it in this article.
An interesting topic about multiple ovarian cysts :

What is polycystic ovary syndrome?
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a condition in which various hormonal disorders occur in women of childbearing age. It affects about 10-13% of women and results in the malfunctioning of various systems in the body, such as :
Lack of ovulation
Excess androgen (too much testosterone), causing symptoms like oily skin, acne, hirsutism, and hair loss
Effects on the cardiovascular system
Increased risk of diabetes
It is a risky condition during pregnancy if left untreated.
What causes multiple ovarian cysts?
The pathogenesis of polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) is not yet fully understood, but it is believed to be caused by multiple hormonal imbalances. Various related disorders and risk factors contribute to the frequency of this condition, including obesity and being overweight in women.
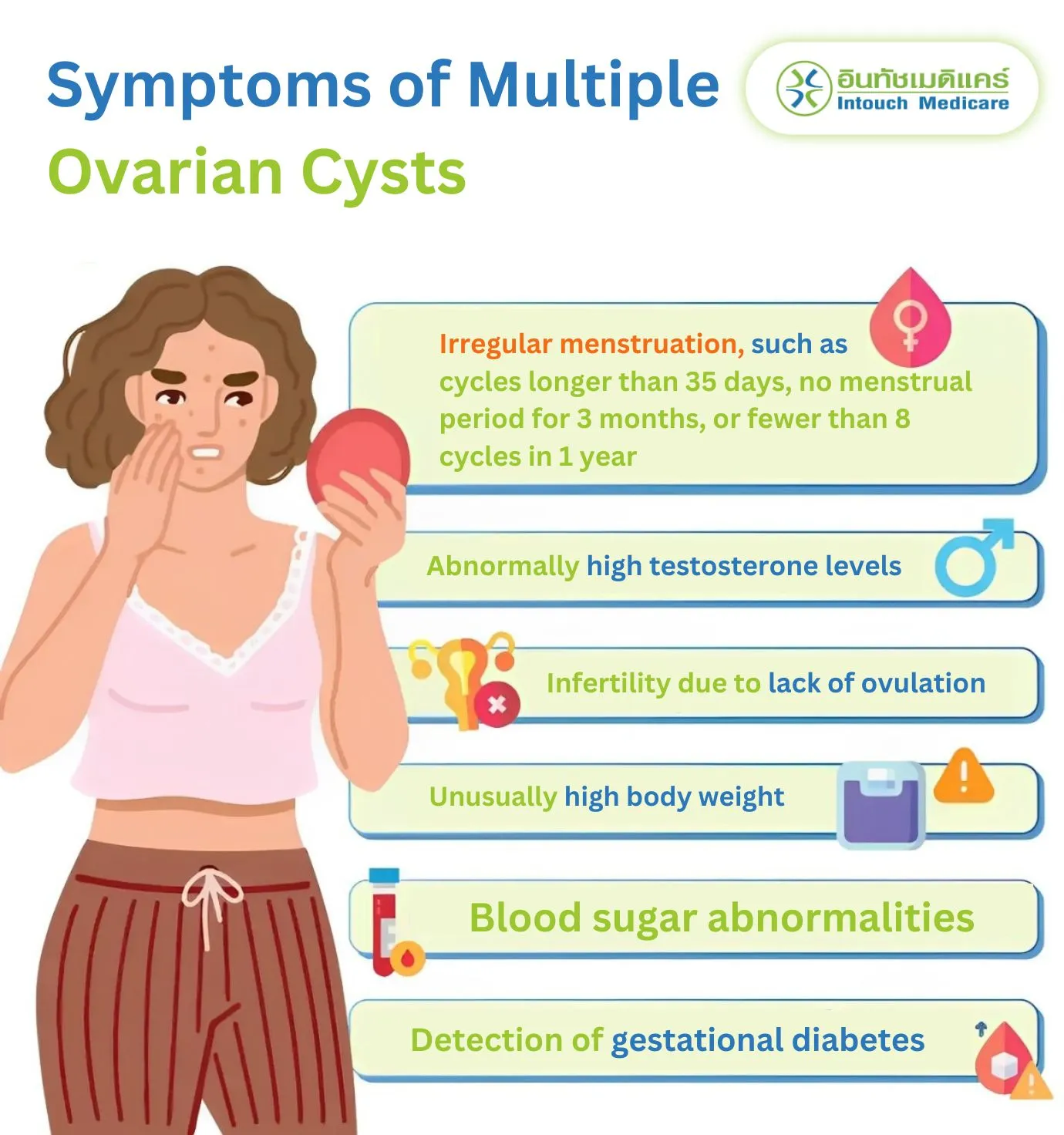
Symptoms of multiple ovarian cysts
Irregular menstruation that indicates abnormal ovulation can occur in various forms. The most common is a menstrual cycle of more than 35 days, a period that doesn't come for 3 months or more, or fewer than 8 menstrual cycles in a year
Symptoms of abnormally high testosterone or high androgen levels include an oily face, acne, hirsutism, and thinning hair. In some patients, the symptoms may not be obvious.
Infertility (trying to have a child for at least 1 year without success)
Abnormally high body weight with a body mass index of more than 25 kg/square meter
Abnormalities in blood sugar, blood lipids, or high blood pressure
Detected gestational diabetes
Read more : PCOS and Pregnancy : What Prospective Parents Need to Know
PCOS diagnostics
To diagnose multiple ovarian cyst disease or PCOS, doctors use a combination of several test methods, including :
1. Ask about menstrual irregularities
The characteristics of irregular menstruation include menstrual cycles longer than 35 days or shorter than 21 days, menstruation that does not occur for 3 consecutive months or more, or fewer than 8 menstrual cycles in 1 year.
2. Physical examination to reveal excessive testosterone:
Preliminary examinations may include :
Abnormal hairiness in areas such as the mustache, beard, chest, pubic region, arms, and legs.
Oily face with large pores.
Abnormally large acne.
Significant hair loss.
In adolescents, there may be more acne and hirsutism compared to adult
3. If the history and physical examination are unclear or if the diagnosis needs confirmation
If the patient's history or physical examination is unclear, the doctor may order blood tests or additional ultrasounds.
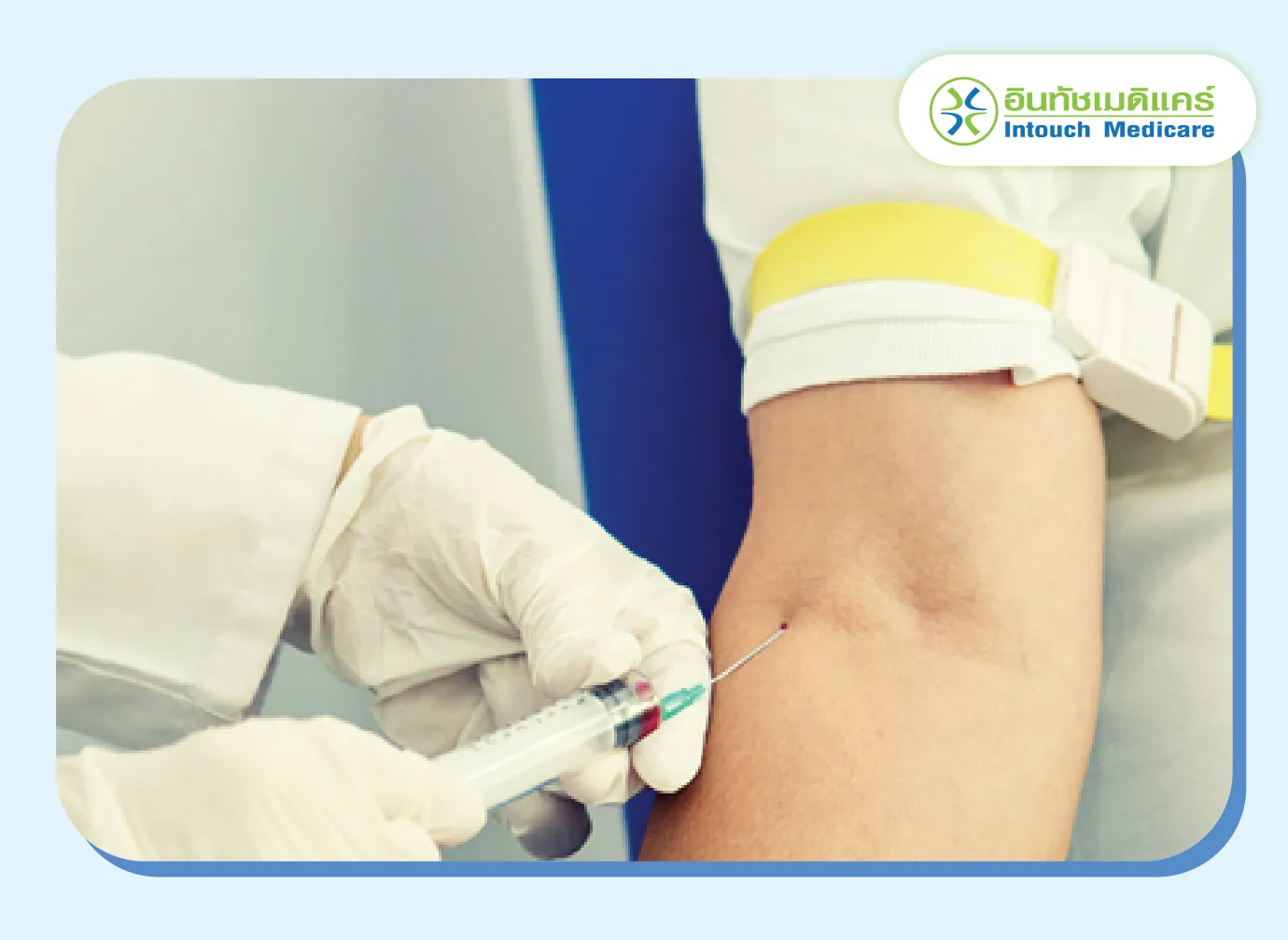
Blood test can determine if the amount of testosterone in the body is abnormally high. This test helps identify other causes of the symptoms, such as thyroid disorders, other hormonal imbalances, adrenal gland diseases, or premature ovarian insufficiency.
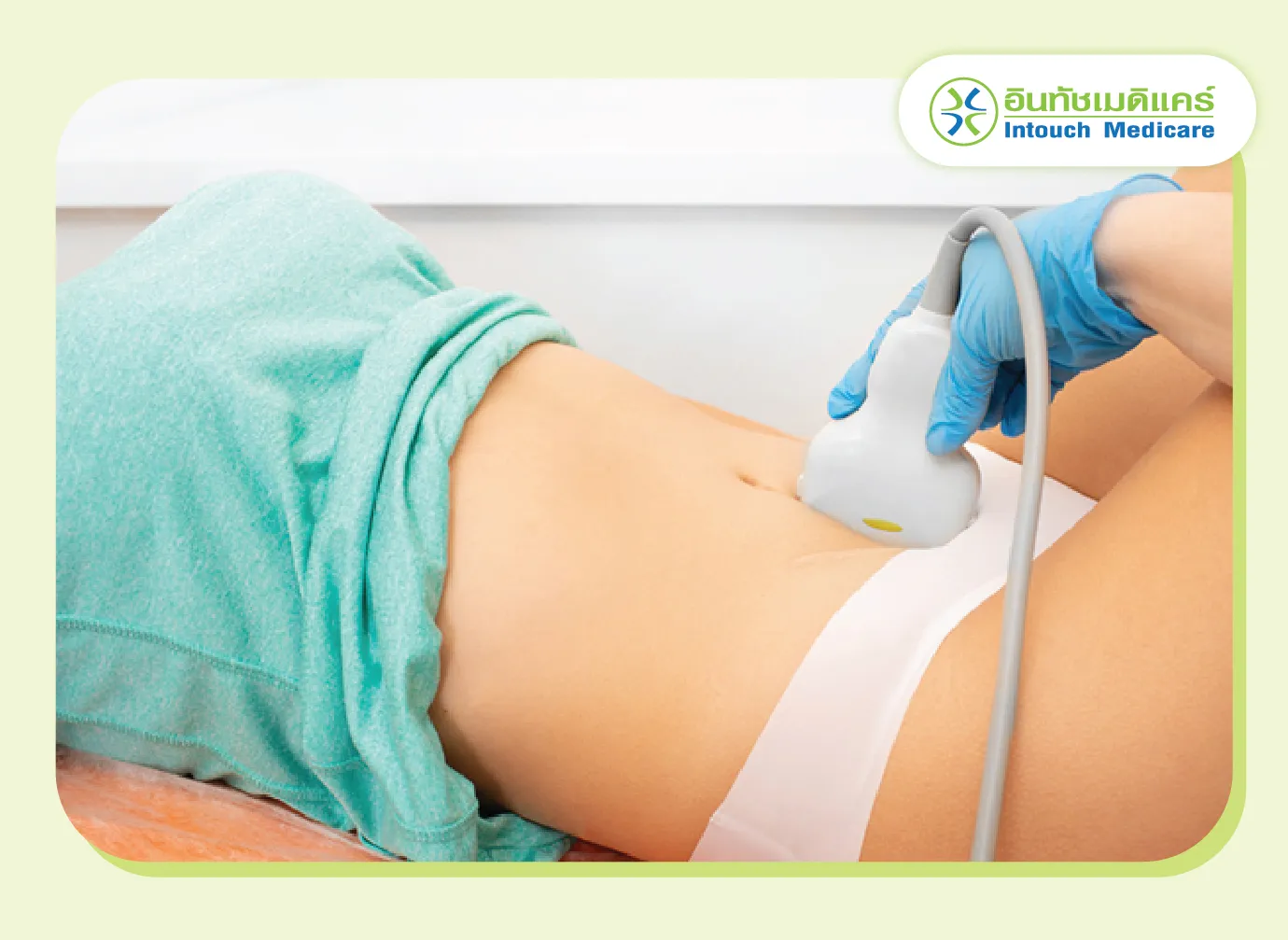
An ultrasound of the uterus and ovaries can reveal the presence of more small cysts than usual in patients with PCOS. Typically, about 10 or more cysts or an enlarged ovarian volume can be observed.
Treatment of cysts in multiple ovaries
The treatment of polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) aims to ensure that patients have normal and regular ovulation, adjust the menstrual cycle, reduce symptoms of excess testosterone, and decrease the risk of diabetes, hyperlipidemia, and high blood pressure in the future.
The main treatment consists of behavioral modification and medication, depending on the patient's symptoms and the doctor's discretion, along with additional tests to assess the risk of other diseases.
""If a general practitioner detects symptoms of irregular menstruation or suspects PCOS in a patient, the case will be referred to a gynecologist for further examination, with the obstetrician and gynecologist in charge of the case."![]()
Behavior modification
Weight control should be recommended for all patients because there is a clear correlation between behavior modification and improvement of PCOS. Studies have shown that a weight loss of 5% from the original body weight is beneficial in many systems.
Dietary control Dietary recommendations focus on healthy foods and reducing starchy and sugary foods, which can lead to insulin resistance.
Exercise Regularly
Treatment by Medication
Medication helps adjust the menstrual cycle, reduce symptoms of excessive testosterone, and decrease the risk of diabetes.
There are many types of drugs that can be used to treat PCOS, including combined hormonal contraceptives, insulin resistance inhibitors, and testosterone-lowering drugs.
"The use of each drug depends on the individual patient and the discretion of the doctor. It is recommended to consult a doctor before starting any medication."![]()
Additional Tests to Assess the Risk of Other Diseases
Patients diagnosed with PCOS should undergo additional testing to assess their risk for other diseases, as PCOS can lead to complications such as prediabetes or diabetes, high blood lipids, high blood pressure, and sleep apnea.
Additionally, some patients may need to undergo further examination for abnormal thickening of the endometrium, which is also associated with PCOS.

How to take care of yourself when you have polycystic ovary syndrome
Observe Symptoms : Pay attention to menstrual cycle abnormalities and acne symptoms on your face. If you suspect you have PCOS, consult a doctor for further testing.

Weight Control and Lifestyle Changes: Manage your weight and change your eating habits. Exercise regularly.
Medication Adherence : If you are prescribed medication, take it regularly and correctly.
Regular Doctor Visits : See your doctor as scheduled to follow up on treatment results.
Monitor for Additional Symptoms : If you notice any new or worsening symptoms during treatment, see your doctor before your next scheduled appointment.
Pregnancy Planning : If you are planning to become pregnant, consult a doctor beforehand. PCOS can affect your pregnancy and baby if not properly managed.
Read more: PCOS and Pregnancy : What Prospective Parents Need to Know
Frequently Asked Questions about PCOS
Can PCOS go away on its own?
Answer: PCOS is a chronic condition influenced by many factors. While it may not go away completely, it can be managed and other complications can be prevented. In patients with mild symptoms, behavior modifications alone may help improve the condition.
However, it is recommended to consult a doctor to evaluate the disease and re-plan treatment because it may be difficult to determine if the disease has improved based on symptoms alone. You may need to have a doctor help you evaluate or conduct additional tests.
Is PCOS dangerous?
Answer: There are long-term dangers. In the short term, there may be irregular menstruation and excessive testosterone levels that can affect the patient's confidence. However, in the long run, if not treated properly, PCOS can result in infertility, diabetes, hyperlipidemia, and high blood pressure. It also increases the risk of endometrial cancer.
"Therefore, it is recommended that all women observe symptoms and seek treatment early to prevent the occurrence of other dangerous conditions in the future."
Do PCOS tests require internal examinations?
Answer: PCOS diagnosis does not typically require an internal examination,
Except in cases where there are symptoms or signs of another disease that necessitate additional internal examination. However, an internal examination is a delicate procedure, and doctors must always ask for the patient's consent. If the patient does not want to undergo an internal examination, it is recommended to consult the doctor to plan treatment together.
Is it necessary to get tested for PCOS every year?
Answer: Currently, there is no clear requirement to test for PCOS every year, but it is recommended to seek examination if you experience abnormal menstruation or other symptoms.
However, it is advised that all women have regular internal examinations and cervical cancer screenings. During these exams, patients will also be asked about their medical history for initial PCOS screening.
Reference
Recommendations from the 2023 international evidence-based guideline for the assessment and management of polycystic ovary syndrome, European Journal of Endocrinology
For more info and make appointment
Hot Line 081-562-7722
Composer : Natthawadi Sriborisut, MD.
Last edited : 13/06/2024

